
Since 2005 AMD has used the Athlon name for their processors. This changed in 2007 when they released their new processor called Phenom. So we must ask the question; what is the difference between the Athlon and the Phenom?
According to AMD, the biggest difference between Phenom and Athlon processors, and in fact any previous processors, is that Phenoms are the first "true" quad core design. Unlike other designs that are multi-chip designs, Phenom is the first processor with all cores on the same piece of silicon die.
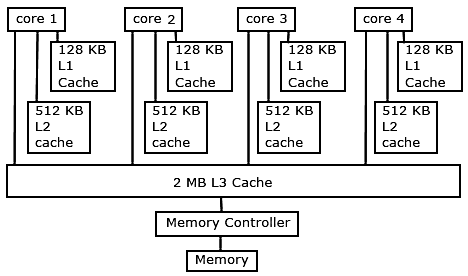
Another difference is the L3 cache in the Phenom processors. This is an additional cache memory that is larger than the L1 and L2 caches, and is shared by all processors. Like the L1 and L2 caches, it provides performance improvements by reducing the number of trips to main memory.
Another difference is HyperTransport 3.0. AMD processors have two external busses, the memory bus is used for communication between the CPU and the memory, and the HyperTransport bus is for communication between the CPU and the motherboard chipset. HyperTransport 3.0 provides greater bandwidth, and more capabilities, compared to HyperTransport 2.0 found on Athlons.
Phenom uses the AM2+ 940-pin micro pin grid array (micro-PGA) CPU socket, which is the successor to Socket AM2 used by the Athlon. The AM2+ socket is backward compatible with Socket AM2, but the the AM2+ socket is needed to support the HyperTransport 3.0 operating frequency.
| Phenom Processors | ||||
| Designation | Clock Speed | Power | Memory | HT Speed |
| Phenom 9500 | 2.2GHz | 95 watts | 1.8GHz | 3.6GHz |
| Phenom 9600 | 2.3GHz | 95 watts | 1.8GHz | 3.6GHz |
| Phenom 9700 | 2.4GHz | 125 watts | 1.8GHz | 3.6GHz |
| Phenom 9900 | 2.6GHz | 140 watts | 2GHz | 4GHz |
The Phenom uses the Stars core microarchitecture, initially known as K10. It uses a 45 nm Manufacturing Process with a nominal operating voltage of 1.1-1.25 Volts. The die size is 285 mm2 and the approximate transistor count is 450 million.
The Phenom introduces Dual Dynamic Power Management (DDPM) which provides separate voltage sources for the processor and the memory controller. The Integrated 128-bit wide memory controller is capable of being configured for dual 64-bit channels for simultaneous read⁄writes. Athlons support up to only 800Mhz DDR2 modules, any faster module is throttled down to 800Mhz. The Phenom memory controller has a separate clock that runs at a fixed rate and so supports modules up to PC2 8500 (1066Mhz DDR2) without throttling down.
More Computer Architecture Articles:
• Multiuser Operating System Functions
• How Computer Chips are Made
• The Fetch, Decode, Execute Cycle
• Basic Decoder Circuitry
• Operating System Memory Paging Hardware Support
• Online Color Coded Resistor Calculator
• Intel Celeron D Processor
• Expanding the Resources of Microcontrollers
• Operating System Memory Allocation Methods
• Intel's Core i7 Processors

